Research in the Malamy lab is focused on epithelial wound healing in the emerging model system Clytia hemisphaerica.
Clytia is a small marine organism of the phylum Cnidaria and class Hydrozoa. Its life cycle includes a sessile polyp form and a medusa (jellyfish) form. Medusa start at less than 1mm and grow to about 0.5cm.
Below you can see a video of a fully grown Clytia medusa swimming happily in a dish in the lab. This medusa is about 0.5cm in diameter.
Clytia as a model for epithelial wound healing
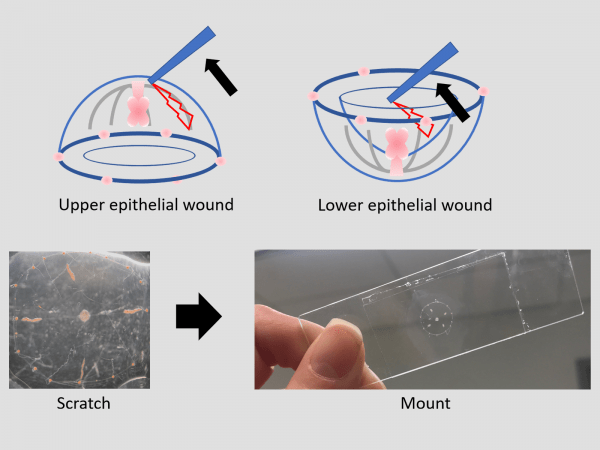
Many features of the Clytia medusa make it an excellent model for studying epithelial wound healing. Epithelial cells form a simple monolayer on the upper surface of the medusa. These cells can be gently scratched to create a wound. The transparency of the system makes it ideal for imaging.
Wounds in Clytia heal very rapidly (~3-6 mm2/min2), 100X+ faster than other reported systems, as seen in this time-lapse movie that spans the 50 minutes after wounding.
This was our first time-lapse movie of wound healing in Clytia – MBL 2015.
__________
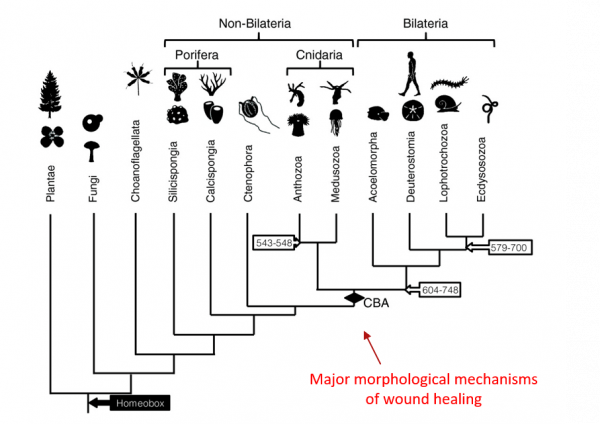
Epithelial wounds heal using mechanisms that have been seen in other invertebrates as well as vertebrates such as ourselves. These mechanisms include:
1. Cell Spreading & Lamellipodia-based Cell Crawling. Total time elapsed: 55 minutes
2. Purse String Closures.
Total time elapsed: 15 minutes
3. Collective Cell Migration.
Total time elapsed: 16 minutes



You must be logged in to post a comment.