“The average worker today stays at each their job for 4.4 years, according to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, but the expected tenure of the youngest employees is half that.” – Forbes 2016
TalentSafe leverages signals from all over the workplace to predict who is at risk of attrition and how to maintain a healthy team.
The break up:
Quitting a job or firing someone is gruelling. However, not all turnover is bad. High employee-retention rate can be evidence of productivity, or alternatively suggest a culture of entitlement or one that fails to challenge employees. There is a healthy, ideal turnover rate applicable to different organizations.
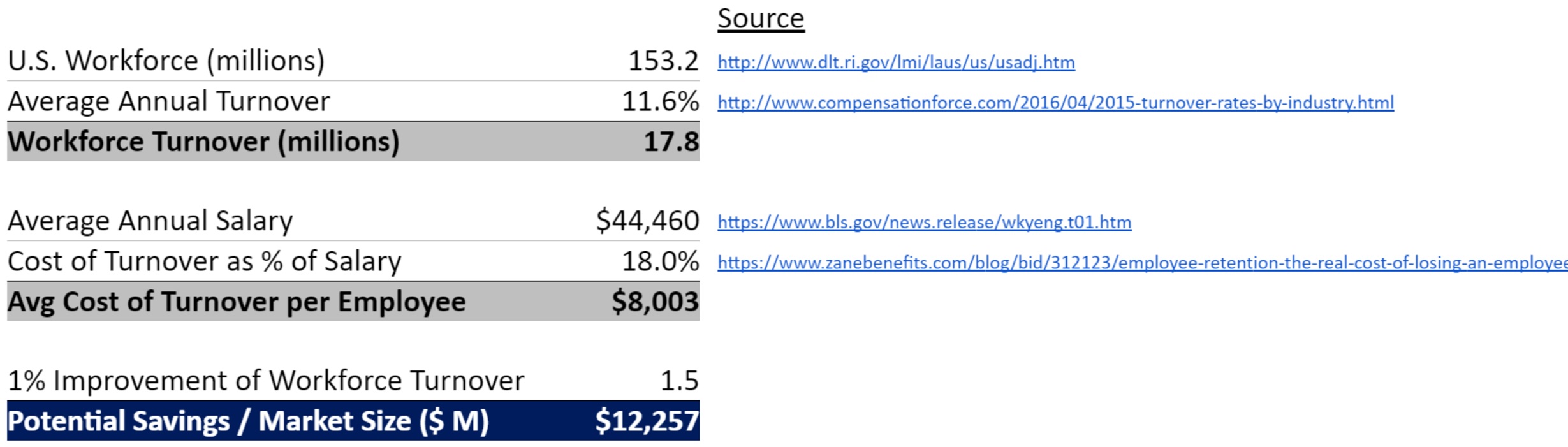
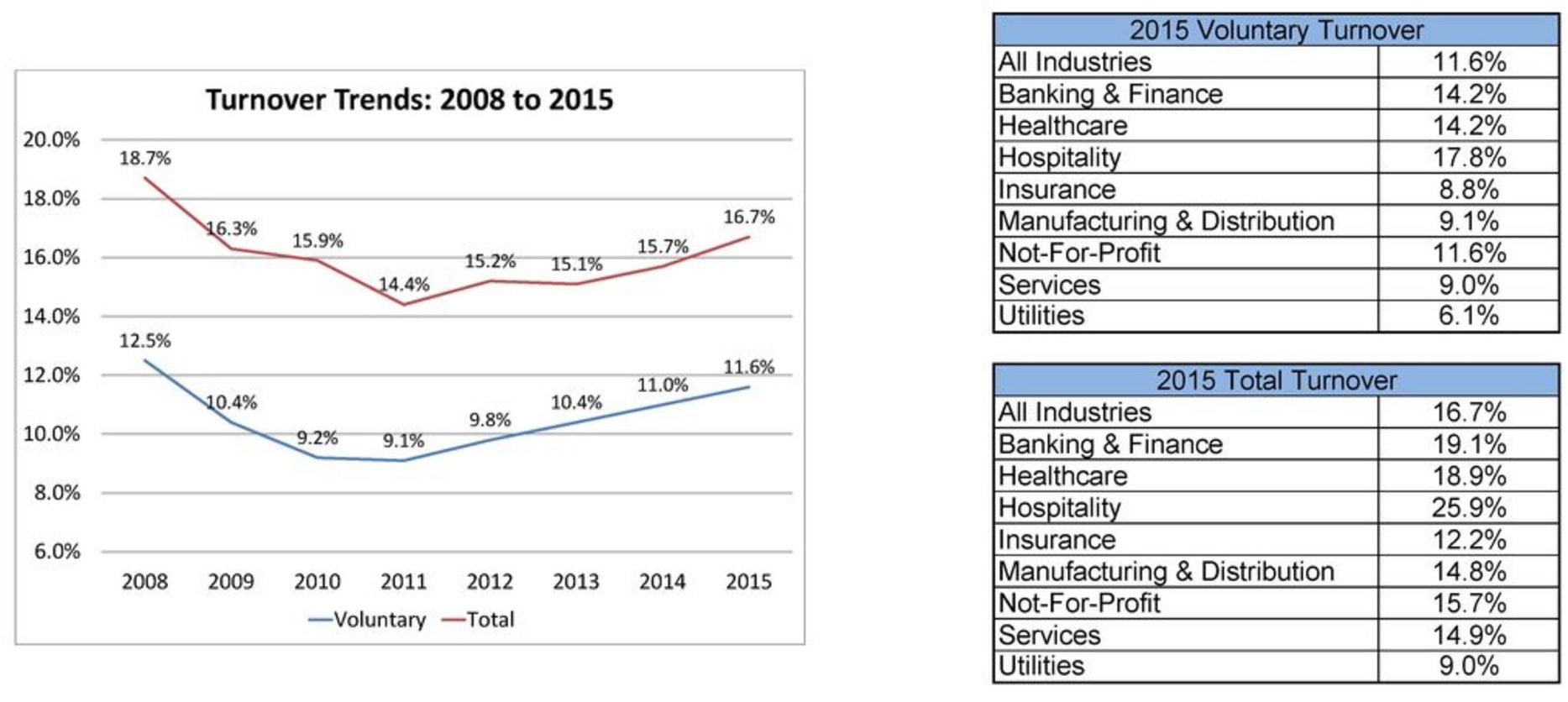 The problem is not small. The potential benefits are massive.
The problem is not small. The potential benefits are massive.
The real problem is how to increase the retention rate of high performance employees and maintain healthy retention rate of other employees.
Solution:
Accurate predictions enable organizations to take action for retention or succession planning of employees. To solve this problem, organizations can use academic research backed machine learning techniques[2] to predict employee turnover. However, no solution exists in the market because of a few gaps that can be addressed.
Fix data gaps:
Modeling data, a big issue, comes from HR Information Systems (HRIS), which are typically underfunded compared to other Information Systems in the organization. This creates noise in the data that renders predictive models prone to inaccuracies. Studies[4] use Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) to improve predictions from the data.
TalentSafe can use data and signals from different sources, such as:
- Baselines from interview process and past experience, using studies[5]
- Biodata
- Employee reference
- Prior job length
- General work-related attitudes
- Self-confidence
- Decisiveness
- Perseverance
- Job-specific attitudes
- Desire for the job
- Overt intent to quit
- Personality traits
- Conscientiousness
- Emotional stability
- Biodata
- Sources of data during the job
- Behavioral and attitudinal
- Emails
- Messages
- Office phone conversation
- Web browsing behavior
- Applications usage
- Job search history
- Meeting attendance, cancellations
- Reimbursements
- Human responses
- Survey feedback from employees, peers, managers, customers
- HR information systems
- Performance ratings
- Performance reviews
- Salary/raise
- Leaders’ feedback
- Employees’ self assessment
- Machine sensors
- Audio detection, video detection, and facial detection from camera
- Behavioral and attitudinal
- Measuring
- Responses – Responsiveness, timeliness, positive/negative emotions
- Motivation – self and others
- Happiness at work place[6] using computer and other systems usage
- Engagement/involvement in work related social events
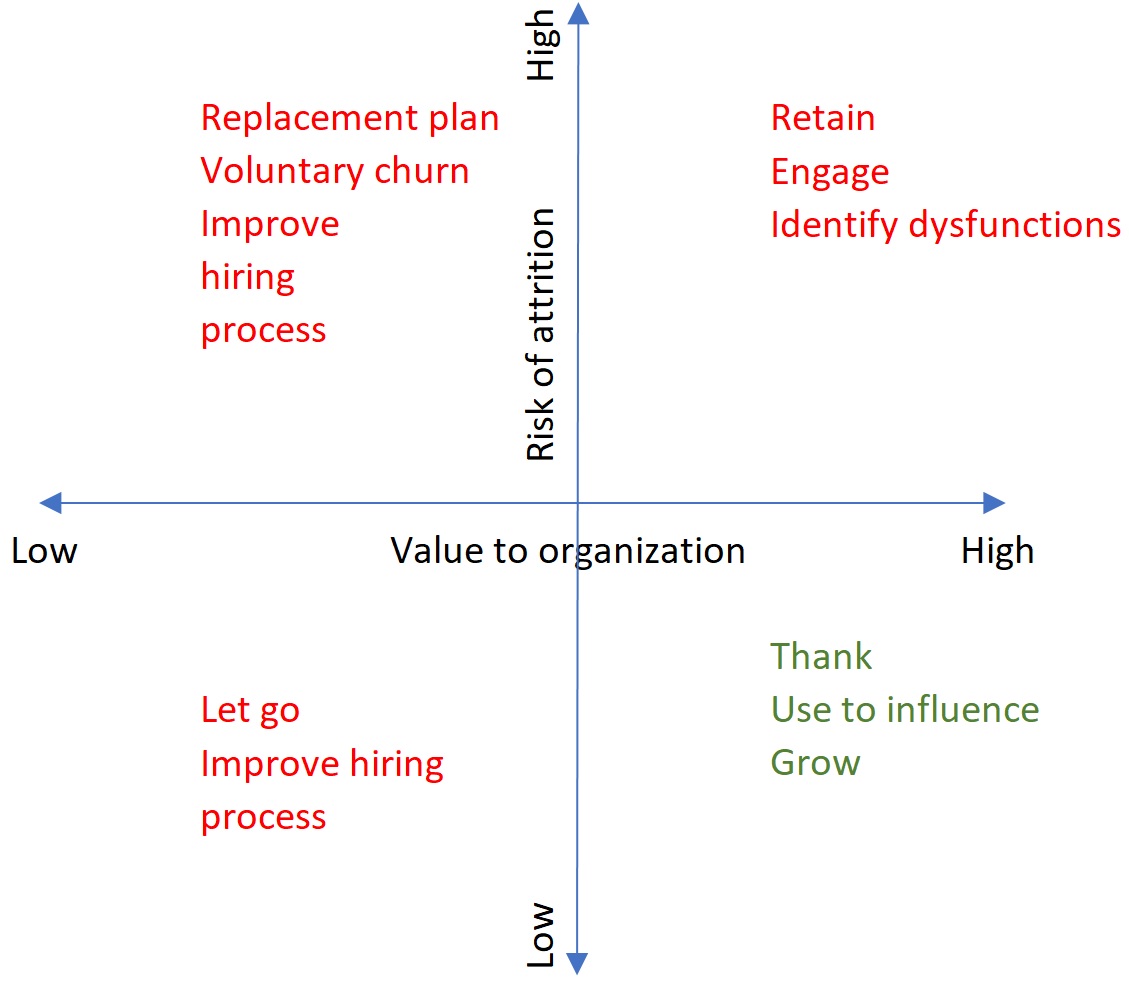
Value of each attrition is different. The departure of VP of Sales has a very different impact compared to an analyst’s.
Benefits > Costs = functional turnover
Costs > Benefits = dysfunctional turnover
TalentSafe’s solution would assess information from all sources to understand sentiments, engagement, and emotions to
- Predict attrition risk
- Assess value of employees
- Recommend the right action plan, and address long term trends and dysfunctions
* value to organization is subject to measurement process like performance metrics
Demonstration / Pilot
Objective: Predict turnovers, understand if the turnover is good or bad, and what kind of action to take. The pilot will be tested in three ways.
- Out of sample: TalentSafe will take all relevant data from a target firm for the previous year including people who stayed and who left. The models will be built on 70% of training data, and 30% testing data
- Out of time: For the same firm, TalentSafe will model using 2016 data and predict on 2017 data
- Real time sample: TalentSafe will cluster different branches of the same organization based on their overall performance and attrition rates & quality. Within each cluster, branches will be randomly assigned into test and control. Nothing changes for control branches, but we implement TalentSafe in test branches to measure the attrition rates and performance before and after implementation.
In all three cases, the assessment will be across metrics of attrition size, quality and performance, in a confusion matrix[7] comparing estimated and actuals.
Once the sources of problems are identified it becomes important to address the root causes. Are there systematic dysfunctions[8] in management/leadership, policies, process, compensation, people etc. that need to be addressed?
— Ewelina Thompson, Akkaravuth (March) Kopsombut, Andrew Kerosky, Ashwin Avasarala, Dhruv Chadha, Keenan Johnston
_____________________________________________

=)