Current Projects in the Lab

Biology of Exosomes
Transfer of biologically active molecules between cells can be mediated by exosomes that are small
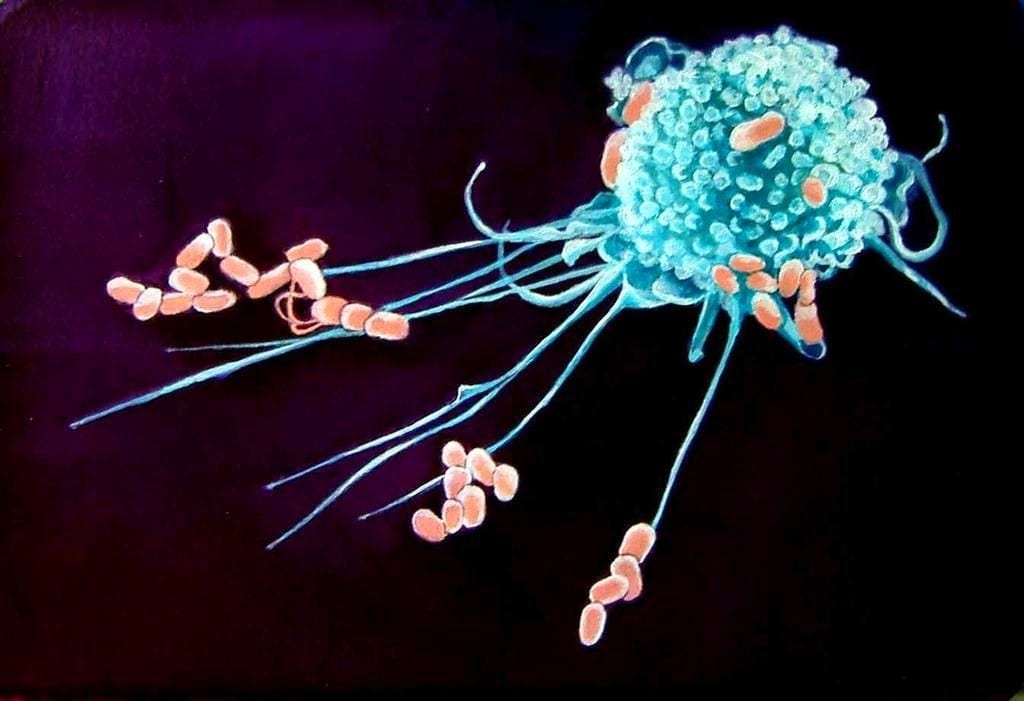
Macrophages and Innate Immunity
Macrophages stand as the sentinels in the lung, fighting bacterial infections as are present in the CF lung. They facilitate the efficient killing of invading bacterial pathogens and remove cells that have undergone programmed cell death. In carrying out these essential functions, phagocytes, including lung macrophages, utilize a select population of ion transport proteins that are expressed in intracellular organelles. Organellar transport proteins control the microbicidal ionic composition of the phagosomes which hold the ingested captured bacteria inside the cell. A critical transport protein which is defective in CF, the chloride ion channel CFTR, renders the lung macrophage unable to carry out its task in killing internalized bacteria.
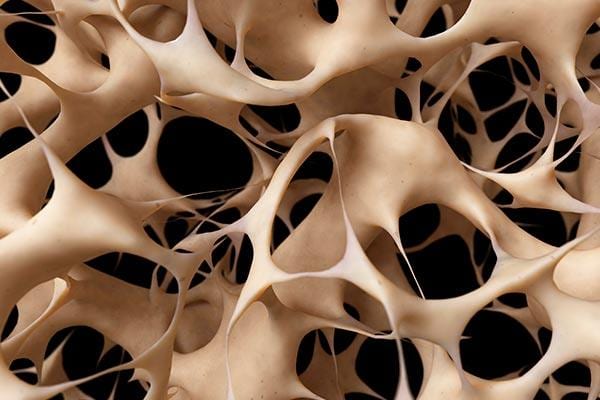
Mechanism of Bone formation
Live bone differs from other connective tissues, including cartilage, in that it is bounded by an active osteoblast layer allowing the bone to create dense lamellar type I collagen, regulate pH and mineral deposition, and regulate water content for an extremely compact and strong structure. Many features of the osteoblast environment are not well described and are only becoming appreciated with
