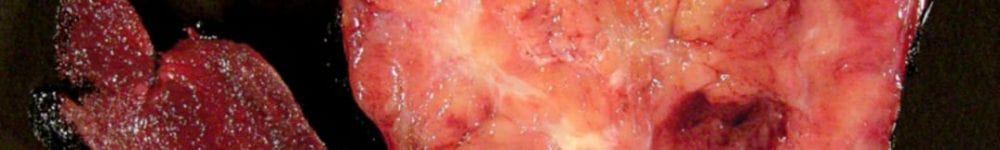
Clinical Info:
- Benign lesions are usually treated by simple oophorectomy.
- Malignant lesions are usually treated by TAH, BSO, omentectomy, and periaortic node sampling.
- Borderline lesions are treated depending on age and desire for preserved fertility.
Hints for Freezing Ovaries:
INK the external surfaces of ALL ovaries, regardless of benign or malignant appearance.
| Gross Appearance | Most Likely Diagnosis | Approach to Freezing |
|---|---|---|
| Smooth-walled cyst with liquid or viscous contents | Serous or Mucinous cystadenoma | Representative wall |
| Cyst with thick bloody contents | Endometriosis | Representative wall |
| Cyst with hair, teeth, chalky material | Teratoma (dermoid cyst) | Representative wall, especially thickened or non-calcified solid areas (to look for immaturity) |
| Cyst with shaggy lining, papillary excrescences | “Borderline” tumor or carcinoma | Representative excrescences or solid area |
| Solid, cauliflower-like | Carcinoma | Representative viable, fleshy, solid area |
| Solid, fibrous | Fibroma / Thecoma | Representative section |
| Solid, fibrous with mucinous cysts | Brenner tumor | Representative junction between fibrous/cystic areas |
| Bilateral fibrous | Metastatic carcinoma (any primary) | Representative section |
| Bilateral mucinous | Metastatic carcinoma (GI primary) | Representative section |